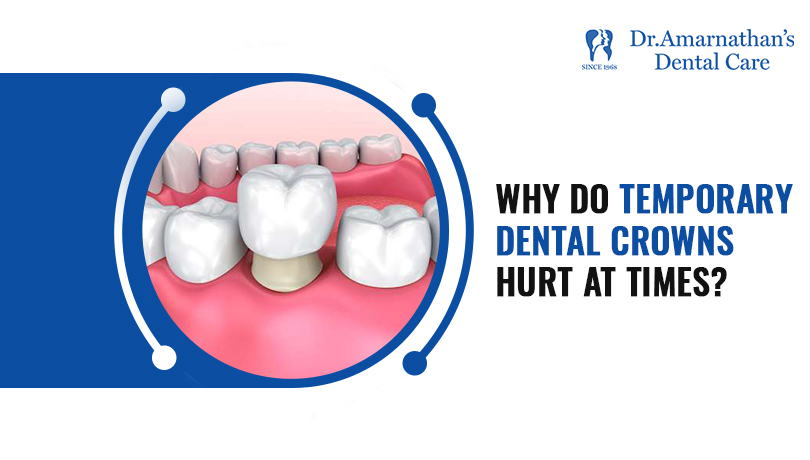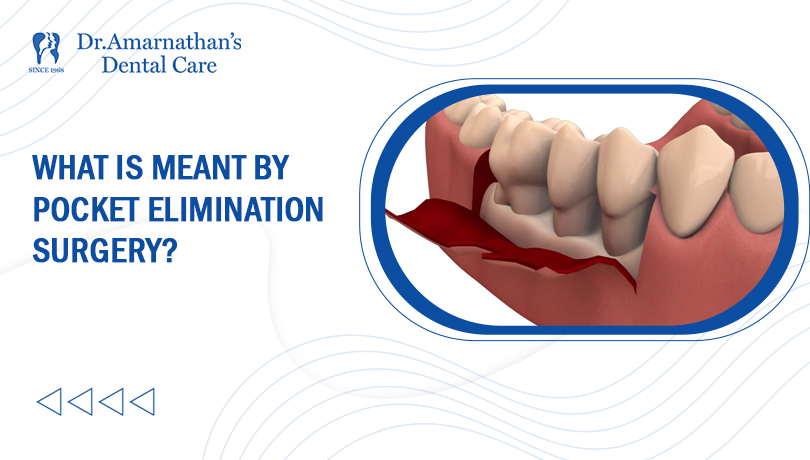
What is meant by pocket elimination surgery?
Pocket reduction surgery refers to a collection of various surgical procedures that tend to remove bacterial collections in the pockets of your mouth. It is also known as Flap surgery, Gingivectomy, and Osseous surgery. It involves folding back the gums followed by eliminating the harmful microbes, calcified substances that exist in that space.
The initial stage of gum diseases can be fixed with simple treatments but invasive procedures are pivotal to treat advanced gum diseases. Pocket elimination surgery is one of the best treatment options to address deep infections in gums.
Why pocket elimination surgery is important?
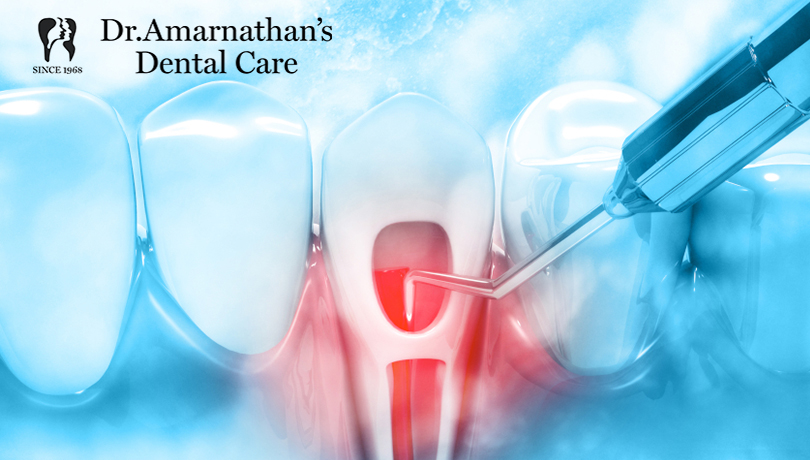
If the bacteria on teeth are not cleaned properly, they move towards the gums and even reach the space around the teeth under the gum line. Such spaces are called periodontal pockets. The surgery aims at disinfecting this region with a combination of surgical accessories, and antibacterial fluids.
Getting rid of harmful microorganisms in gum pockets provides the following benefits:
- Prohibits the progression of bacteria – The bacteria growth in gum pockets will enter the bloodstream if they breed. It is connected to various serious conditions such as heart diseases, stroke, etc. It means pocket reduction surgery protects your vital organs also from bacteria invasions.
- Halt bone loss – Once the microbes enter gum pockets, they deepen the region, affect gum tissues and even weaken the jaw bone. In such cases, the teeth lose their bone support and eventually fall out. Thus pocket elimination surgery safeguards your teeth and prevents tooth loss.
Pocket elimination surgery is a thorough cleaning process that cleanses the regions in your mouth that are incredibly difficult to clean. Besides refreshing your mouth by eliminating microbes, this treatment empowers you to tackle various harmful effects of oral bacteria.
What does pocket elimination surgery involve?
The process begins with assessing the condition of teeth, gums, and underlying bone using x-rays and other dental assessments. Then the depth of the gum pocket is measured using an instrument called a periodontal probe. If the dentist detects if a periodontal pocket is greater than 5 millimeters, then he/she will prescribe this surgery.
Similar to other invasive dental treatments, gingivectomy is also performed after administering local anesthesia. The steps involve:
- An incision is made in the gum flap and it is gently pulled back to access the roots. It exposes the bacteria build-up and plaque deposits in those spaces.
- Now the dentists remove the bacteria from the tooth roots and diseased gum tissues.
- Then, the irregular root surfaces are smoothened to prevent bacteria accumulation near the root again.
- Thus the depth of the periodontal pocket is reduced and the gum flap is sutured. It will heal within 2 weeks.
What should you do after the pocket reduction surgery?
Following the surgery, the treated region is covered with a bandage. You would sense mild pain and swelling. They are normal and go away in the following days. For the 48 hours following the surgery, it is important to take anti-inflammatory medications, do mouth rinse with antibacterial mouthwashes to keep the area clean.
Similarly, you will receive a list of aftercare instructions from your dentist. You should stick to that guidelines. They speed up the healing process and reduce the risk of infections at the surgical site. The common aftercare activities you should follow after a pocket elimination surgery involve:
- Take soft foods for a few weeks
- Get regular cleanings and check-ups from your dentist
- Take the prescribed painkillers alone
How do you know whether you need pocket elimination surgery?
In general, the periodontal pockets are 1 to 3 millimeters deep and do not bleed. When oral microbes penetrate the region, the depth is increased. If you sense bad breath in your mouth whilst encountering bleeding and swelling in your gums, they might be a sign of bacteria accumulation in the space between the teeth and gums.
You might have an infection in your gums as well. You should consult your dentist immediately.