What are Eruption Cysts? Know about Causes, Symptoms and Treatment
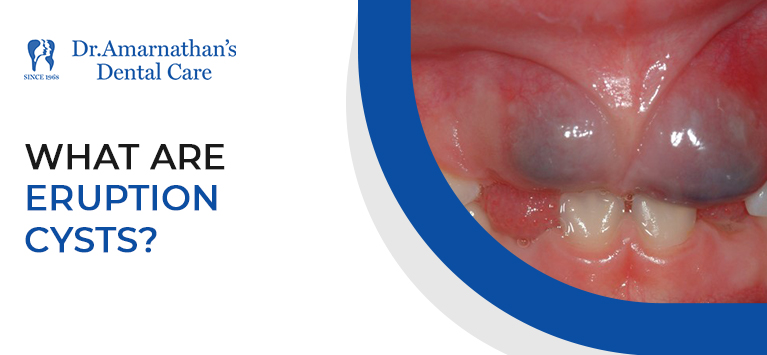
Blue pimples called “eruption cysts” occur as a permanent tooth emerges (breaking through the gum line).
On the mucosa of the tooth, benign cysts called eruption cysts and eruption hematomas develop. These soft gum tissue lesions, lumps, or bruises have a dome-like structure. They have a transparent appearance and a reddish-brown or bluish-purple hue.
Although the reason of them is unknown, it could be due to early childhood caries (baby bottle tooth decay), damage from hard food or brushing, a lack of room for the tooth to erupt, or a hereditary predisposition2.
There is no cause for concern with an eruption cyst. They typically emerge four days before the tooth appears, are ruptured as the tooth emerges, and then recover a few days later. According to a modest study, your upper jaw’s maxilla, which houses your primary molars, is where most eruption cysts manifest themselves.
What causes Eruption Cysts?
When blood or fluid builds up around a tooth that is erupting, an eruption cyst results. Cysts that cause eruptions sometimes seem to materialize overnight.
They can develop as a result of sucking on the gums, like all oral cysts.
The majority of the time, ovarian cysts heal on their own. The baby’s tooth will likely burst the sac as it erupts as it grows in.
A regular dentist may make a small incision to empty the cyst and expose the tooth so it can grow in if the tooth doesn’t break through the gum tissue layer within a few weeks.
Eruption cyst symptoms
Cysts from an eruption can be unpleasant and ugly. Fortunately, most eruption cysts won’t hurt when they explode.
The following signs of an eruption cyst include:
- A reddish-brown or bluish-purple lump, lesion, or bruise over a tooth that is erupting
- The tooth that is not growing properly
- Painful or unpleasant tongue odor brought on by an infected eruption cyst
Treatment
Eruption cysts don’t normally involve treatment because the majority of them should be left alone. They’ll probably burst all by themselves.
A small surgical incision may be indicated to evacuate the eruption cyst if it does not naturally dissolve after a few weeks.
Although it may sound unpleasant, this is a routine surgery that is typically carried out under local anaesthetic and doesn’t call for any recovery time.
In order to treat any possible infections in the eruption cyst, the dentist may also recommend medication.
Bottom line
Eruption cysts and the dentigerous cyst, another type of dental cyst, may be mistaken. These fluid-filled sacs also develop over immature teeth. An eruption cyst is popped and heals once the tooth emerges, however a dentigerous cyst frequently forms when a tooth cannot erupt properly and may require dental treatment to repair. A dentigerous cyst is typically removed surgically or via the draining technique called masupialization.