Teeth and Gums: Structure and Function
The health of your digestive system depends on the health of your teeth and gums. It would be a good idea, therefore, to know about the basics of the structure and function of your teeth and gums.
Your teeth
The functions of your teeth are to cut and tear, crush and mash, grind and break up food items in order that they become easily digestible. There are two rows of teeth opposite each other, one in the upper jaw, and the other in the lower jaw. The repeated movement of the jaws, keeping the food items between the teeth, carries out these functions.
Children develop first the primary teeth, also called ‘baby teeth’ or ‘milk teeth’. These are temporary teeth, usually twenty in number. They fall out, and are replaced by permanent teeth, as children grow to become adults. When the maturation is complete, adults have in place thirty-two permanent teeth, classified as follows.
Incisors
The incisors are the front teeth, eight in number, four in the upper jaw and four in the lower jaw. They have the shape of a shovel with a sharp cutting edge. Their main function is to cut food into smaller parts.
Canines
Two canines are located in the upper jaw, one on either side of the group of front teeth. Two more are located likewise in the lower jaw. Thus, there are four canines in all. They resemble those of a dog or a vampire. The canines serve to tear food.
Premolars
Four premolars are located in the upper jaw, two adjacent to the left canine, and two adjacent to the right canine. Four more premolars are positioned in the lower jaw in a similar way. Hence, the total number of premolars is eight. They are properly shaped to grind food materials hard.
Molars
They are the largest teeth you have. They are placed in the upper jaw, deep into the mouth, three in a row next to the premolars on the left side, and three in a row next to the premolars on the right side. Likewise, six more molars are located in the lower jaw. Thus, the total number of molars is twelve. Their main function is to grind food.
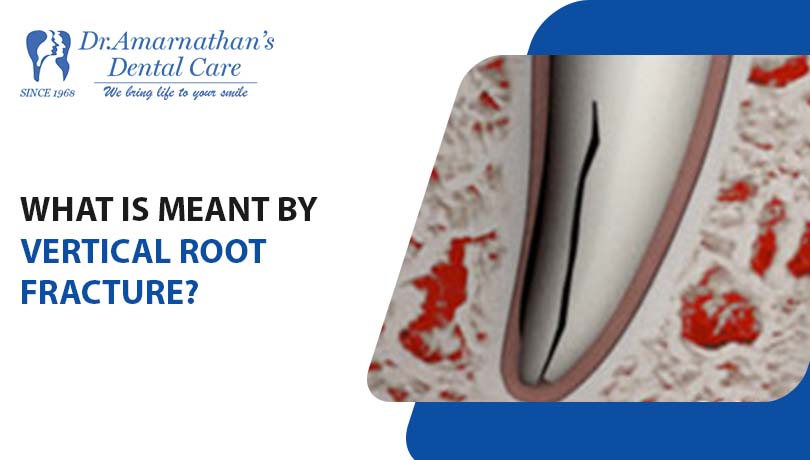
Parts of a tooth
Each tooth has a crown above the gum line, a root fixed below the gum line, and a neck between the crown and the root. Enamel is the hard substance that covers and protects the crown.
The soft interior cavity is called pulp. Cementum is the thin layer of bone, which covers and protects the root. Dentin is less hard than the enamel, and it forms the major portion of a tooth; it lies beneath the enamel and the cementum.
Your gums
Gums, medically known as gingiva, are a soft tissue that surrounds and seals tight your teeth. They are tightly bound to the underlying bone. They protect the deeper tissues from the friction of hard food items, when they are broken down to pieces. Good gum health is essential for good dental health. Massaging of the gums activates increased circulation of blood, which is a healthy exercise for the gums.