Cheek biting – Types, Causes, Side effects and Treatments
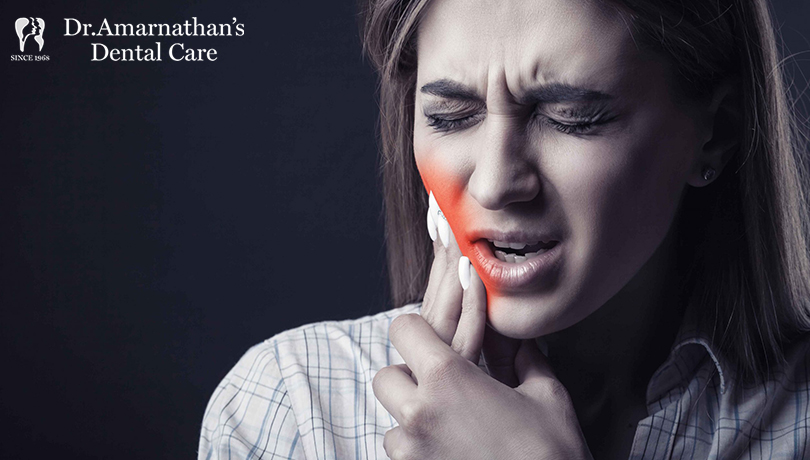
Biting your cheeks repetitively seems like a harmless body-focused repetitively behavior (BFRB) similar to nail biting and hair pulling. Such chronic cheek biting, scientifically known as morsicatio buccarum is a stress-related habit that corresponds to obsessive-compulsive disorder, stress and anxiety.
Do you know? This is a self-destructing habit as it injures the oral tissues and put your dental health at stake. As this habit starts in late adulthood and extended into adulthood, many kids, teenagers and adults develop serious dental health concerns over chronic cheek biting and chewing.
Keep reading to know more about its harmful consequences and ways to overcome this fatal habit.
Types of cheek biting
The cheek biting habit is classified into 5 types as follows:
1) Accidental cheek biting – Biting your cheeks unexpectedly while eating or chewing. It is not the same as chronic biting but causes injury and inflammation at the bite location.
2) Regular accidental cheek biting – The accidental cheek bites will require dental attention if it occurs repeatedly. If you encounter such unexpected cheek bites frequently, then you might have teeth misalignment or jaw problems like TMJ disorders.
3) Cheek biting while asleep – It can also be caused by sleep disorders like sleep apnea but can be addressed with appliances like bite-guard.
4) Habitual Cheek biting – You bite your cheeks as a routine behavior mindlessly.
5) Chronic Cheek biting – The compulsive cheek biting activity is categorized as BFRB when you cannot stop even after attempting to break this habit.
What are the hazardous effects of chronic cheek biting?
To put it simply, cheek biting is triggered by stress, ill-fitting dental appliances, teeth misalignment, jaw problems or as a responsive behavior. Whatever the cause is, the cheek biters damage their mouth tissues that lead to serious health concerns. The common side effects include:
- In general, the cheek biters have a favorite location on their inner cheeks. Constant biting would break the skin on that specific spot and make it paler, smoother than the surrounding tissues. It leads to irregular lineage in cheeks and is followed by inflammation with purple spots.
- As the skin becomes soft because of repetitive biting, the underlying tissues can easily get damaged which leads to mouth ulcers.
- In certain cases, soft tissue erosion also occurs with chronic cheek biting.
- People with cancerous cells easily develop oral cancer with this self-destructive activity because chronic mechanical irritation activities like inner cheek biting aid in oral carcinogenesis progression.
Apart from the jagged sensation and self-inflicted injuries, this habit affects the cheek biters emotionally as they may feel guilt, shame and low concerning their damaging habit. It may push them to limit engaging their social activities.
How can I stop biting my inner cheeks?
The cheek biters are not aware of this habit with stress. Luckily, this problem can be addressed and treatment options are available to break this habit.
Sometimes, orthodontic treatment or corrective jaw surgery treatments are mandatory to address this issue. Besides this, the dentists derive a treatment after determining whether the cause is habitual or compulsive.
The treatment options available to stop this damaging behavior include:
- Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT)
- Acceptance and commitment therapy
- Dialectical behavioral therapy, or DBT
- Comprehensive behavioral treatment
- Habit reversal training
Bottom line
Inner cheek biting is a self-injuring habit that has its stem from depression in most cases. Meanwhile, teeth dental alignment problems also push one to bite cheeks periodically. If it is not addressed on time, it will have damaging effects on our health. Breaking this habit is also possible with the right treatments and practices once the triggers are identified.