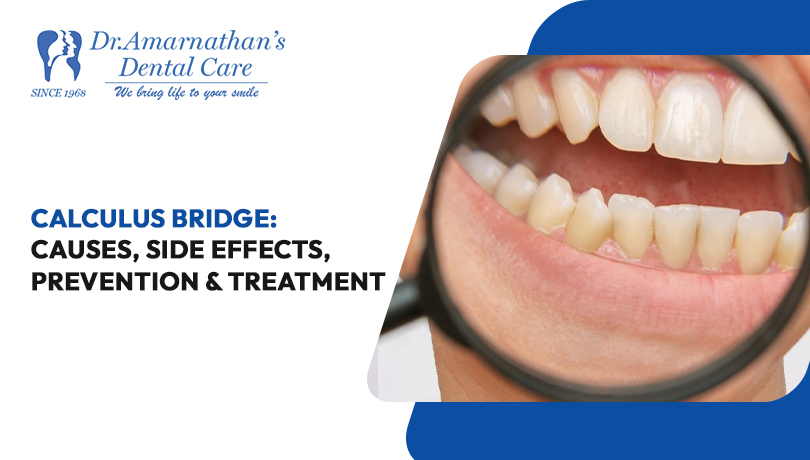
Calculus Bridge: Causes, Side Effects, Prevention & Treatment
Calculus Bridge is a frequent dental problem that can cause discomfort and suffering to people. It happens when plaque and germs accumulate on the teeth, forming a bridge-like structure between two teeth. It can result in a range of side effects, including tooth decay, gum disease, and tooth loss. In this post, we will look at the causes of the calculus bridge, the potential side effects, and how to prevent and manage this condition for good dental health. Understanding the basics of calculus bridge can help individuals take proactive measures to protect their teeth and maintain a healthy smile.
What is Calculus?
Calculus refers to dental calculus, often known as tartar. It is a firm deposit that occurs on teeth as plaque (a soft bacterial film) mineralizes. Calculus develops differently for each individual, depending on the pH, calcium concentration, and other factors in their saliva.
What is Calculus Bridge?
A calculus bridge is a hardened plaque and tartar structure that connects two or more teeth. It refers to the accumulation of hardened plaque, or calculus, on the surface of the teeth.
How does the Calculus Bridge form?
Plaque forms when food particles and saliva come together in the mouth. If you do not brush correctly after meals, food will build up and settle on your teeth.
Plaque is a sticky, bacterial film that forms on teeth. If plaque is not removed by brushing and flossing, it can harden into tartar.
Tartar is more difficult to remove than plaque and can build up over time, forming a calculus bridge.
Causes of Calculus Bridge?
Various elements influence the creation of calculus bridges.
Poor oral hygiene: Inadequate oral hygiene can lead to the collection of plaque and bacteria, resulting in calculus bridge formation.
Dry mouth: xerostomia can also contribute to this problem because it reduces salivary production, increasing germs and plaque buildup.
Brushing Habit: Improper brushing can cause plaque and calculus bridging.
In addition, practice proper dental hygiene to maintain your teeth healthy. Brush your teeth after smoking to keep them cleaner, especially if you have crooked or crowded teeth.
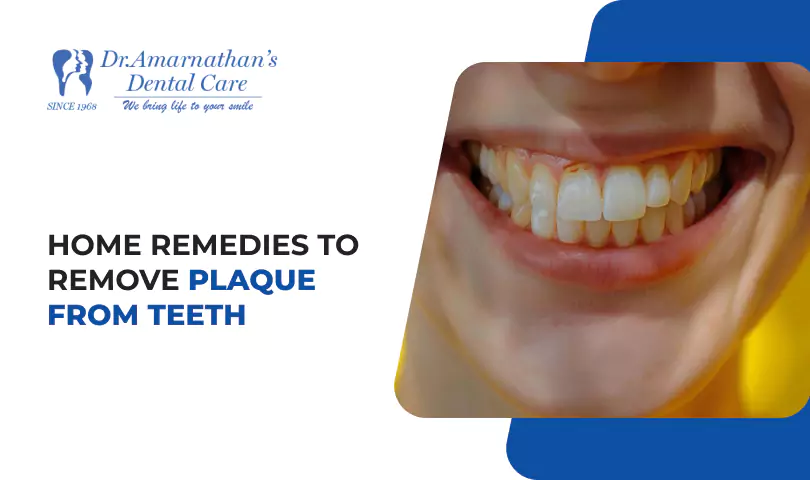
Brushing and flossing can help remove plaque. Calculus cannot be removed by brushing alone, and waiting too long between dental visits can raise the chance of a calculus bridge. Addressing these factors helps to reduce the possibility of developing calculus bridges and preserve good oral health.
Side Effects of Calculus Bridge:
An untreated calculus bridge can lead to side effects and the development of more severe conditions.
Gum Disease: Tartar in the gums can cause gingivitis. Gums that are bleeding, red, or swollen are primarily the result of tissue inflammation.
Tooth loss: Untreated tartar might cause tooth loss.
Halitosis: The presence of tartar promotes the growth of germs in your mouth, which can produce bad breath.
Tooth color: Tartar staining can cause it to turn black or brown.
Cavity: Plaque and tartar can also build tiny holes in your teeth’s enamel, allowing germs and acid to remain inside and cause cavities.
Periodontitis: Periodontal disease is a severe gum infection that can cause lifelong bone loss around the teeth.
Treatment for Calculus Bridge:
Once you have a bridge of hardened plaque or calculus on your teeth, you cannot clean it away. A dentist or dental hygienist will have to remove it.
Dental Examination: Before the cleaning, your dentist or dental hygienist will check your teeth and gums to determine the amount of calculus accumulation and any signs of gum disease.
Scaling: The dentist or dental hygienist will use specialized dental instruments to delicately scrape away calculus from the tooth surfaces, both above and below the gumline. This procedure may use both manual scaling tools and ultrasonic machines that use vibrations to loosen and remove the calculus.
Root Planing (if necessary): Root planing may be performed in cases of substantial calculus formation and associated gum disease. Smoothing down rough spots on the tooth roots helps to remove bacteria and reattach the gums to the teeth.
Polishing: The teeth are polished to eliminate any residual plaque and calculus stains, leaving the tooth surfaces smooth and clean.
Fluoride Treatment (optional): In some instances, a fluoride treatment may be used to strengthen teeth and prevent decay.
It is essential to know that frequent brushing and flossing alone will not successfully remove dental calculus. Professional dental cleanings are required to safely and thoroughly remove calculus deposits and maintain good oral hygiene.
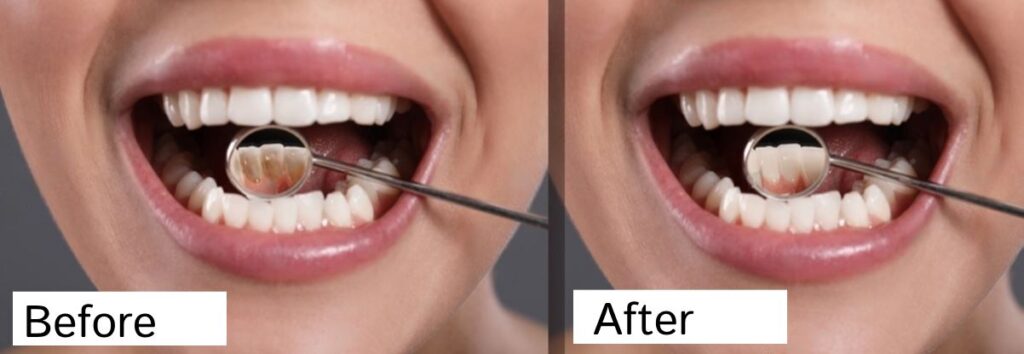
Prevention of calculus bridge
Maintaining good dental health prevents plaque from converting into calculus, which includes the following.
- Brush your teeth thoroughly twice daily using fluoride-containing toothpaste.
- Changing your toothbrush every four months can help avoid calculus bridges.
- Every day, clean the spaces between your teeth. This process, known as interdental cleaning, may include flossing or using another tool to remove dirt from between your teeth.
- Eating meals high in vitamin C helps to eradicate bacteria and foul breath from your mouth.
- Limit sugary beverages and snacks. If you limit your intake of sugary foods, there will be fewer possibilities for bacteria in your mouth to combine with the sugar that remains and produce plaque on your teeth.
- Regular checkups are advised if you receive in-office dental cleanings at least once or twice a year. If you have periodontal disease, you may need more frequent checkups.
Takeaway
To summarize, comprehending the subtleties of a “Calculus Bridge” in dentistry emphasizes the need to remove calculus buildup from teeth. Exploring the reasons, potential side effects, and prevention techniques emphasizes the importance of maintaining proper dental hygiene. Regular dental checkups and expert cleanings are essential for the best treatment and prevention. Individuals can achieve a calculus-free smile and improve their entire well-being by being knowledgeable and proactive about their oral health.
Frequently Asked Question
-
Is calculus bridge harmful?
-
Is it good to remove calculus from teeth?





https://pq.hosting/vps-vds-nigeria-abuja